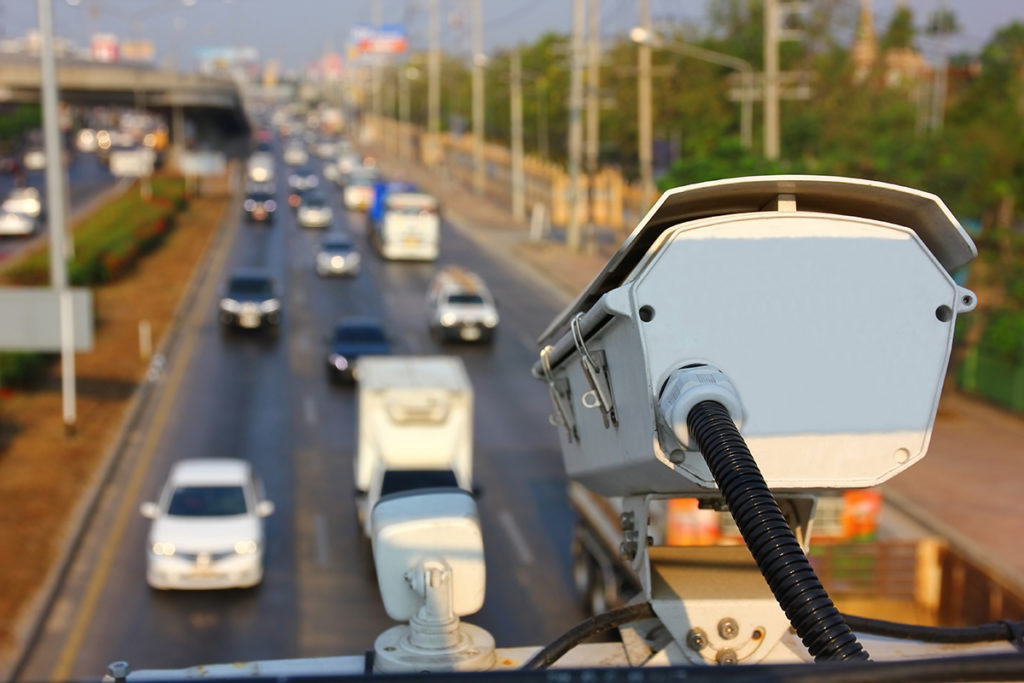
Closed-circuit TV (CCTV) systems use coaxial cable, wireless technology, and fiber-optic cable to transport the cameras’ signals to the monitor. Fiber-optic cable is a good choice when there is a high likelihood of off-air interference such as power lines or nearby Radio Frequency (RF) transmitters. Fiber-optic cable is also the solution for very long CCTV transmission links of more than 300 feet. Fiber-optic cable also can improve reliability and reduce maintenance costs. CCTV cameras and monitors are typically looking for RF signals, so in order to use fiber-optic (light frequency) signals, your CCTV system must have fiber-optic cable and connectors, a fiber-optic transmitter and a matching receiver. The transmitter and receiver also converts the normal RF signals to light frequency signals to give your camera and monitor the signals they need to operate. (Source: ItStillWorks.com)
The main factors that should prompt the installer to consider the use of fiber optic transmission in a CCTV system (Source: Dipol):
- Long cable runs
- Several or more cables running in parallel
- Narrow cable shaft
- Industrial environment, electromagnetic interference
- The possibility of surges, overvoltages
- Risk of dampness
The Fiber School provides a specialty fiber installer course that focuses on today’s CCTV systems which are IP addressable and considered to provide interactive and intelligent video surveillance. Students will learn about the concepts of video surveillance, the selection of components and how they are deployed within home and business. Also included are options for implementation over Local and Wide Area Networks (LANs & WANs) and various cabling TR-CCTV Closed Circuit TV Specialized Installer infrastructures.
The CCTV Specialized Installer Course will allow students to:
- Install and configure interactive video surveillance
- Attach any number of network-connected cameras
- Become familiar with closed-circuit camera systems